What are the causes of hip fractures?
Common causes include a fall in the house and accidents. A fall from standing position is the most common reason for a hip fracture among the elderly. Fracture will not occur without a fall, even if there is severe osteoporosis. Rarely one may have a hip fracture happen spontaneously. Weak bones (osteoporosis) is the leading cause of hip fracture.
Risk factors for hip fractures
Age. Age is also a major risk factor. The risk of hip fracture rises with age. Because bone density (Osteoporosis) and muscle mass (called as sarcopenia) tend to decrease with age especially in females after menopause. Older people can also have problems with vision and balance, which can increase the risk of falling.
Sex. Hip fractures in women are more often than in men. Women lose bone density faster; because of hormonal changes in the body. Drop in oestrogen levels accelerates bone loss. However, men also can develop dangerously low levels of bone density.
Osteoporosis. Is common in elderly persons and causes bones to weaken with increased risk of fractures.
Other chronic medical conditions. Endocrine disorders, such as an overactive thyroid or parathyroid glands can lead to fragile bones. Hyper-Parathyroid is an important cause of bone loss.
Affection of the brain and nervous system cause cognitive impairment, dementia, Parkinson’s disease, stroke, peripheral neuropathy, weakness of muscles and imbalance and increase the risk of falling and hip fracture.
Certain medications. Corticosteroids such as prednisone can cause osteoporosis and brittle bones. They are usually given in diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and asthma. Certain drugs can make a person dizzy and more prone to falling. Sedatives and anti-depressants are often associated with falls.
Nutritional problems. Deficiency of protein, calcium and vitamin D in diet in children lowers peak bone mass and increases risk of fracture later in life. It’s also important to get enough calcium and vitamin D in older age to try to maintain the bone mass.
Body mas index ( BMI) Low body weight increases the risk of bone loss.
Physical inactivity. Lack of regular exercises, such as walking, weight-training and calisthenics such as Surya- namaskar can result in weakened bones and muscles, causing falls and fractures more likely. Sitting for a long time reduces bone mass.
Tobacco, caffeine and alcohol use. can interfere with the normal bone formation, resulting in bone loss.
How to prevent hip fracture?
1.Life style. By balanced diet and exercises to strengthen bones to prevent falls and osteoporosis. Healthy lifestyle choices (balanced diet and proper exercises) from early childhood build a higher peak bone mass and reduce your risk of osteoporosis and hip fracture in later years. Peak bone mass achieved till the age of 30 years. After 30 the bone mass starts decreasing. The same measures (diet and exercises) adopted at any age, even in nineties, lowers your risk of falls, osteoporosis and sarcopenea (weak muscles) and improve your overall health.
2.Diet Balanced diet consists of high protein, enough calcium and vitamin D. As a general rule, men and women age 50 and older should consume 1,200 milligrams of calcium a day, and 600 international units of vitamin D a day and protein 1gm per kg weight.
3.Exercise to strengthen bones and improve balance. Weight-bearing exercises, such as walking, help you maintain peak bone density. Exercise also increases your overall strength, making you less likely to fall. Ideal age to start exercises is from early childhood. Peak bone mass is achieved at age 30; then bone mass decreases. Balance training also is important to reduce your risk of falls, since balance tends to deteriorate with age.
4.Avoid smoking or excessive drinking. Tobacco, caffein and alcohol use can reduce bone density. Drinking too much alcohol can also impair your balance and make you more likely to fall.
- Prevention of fall. Fracture will not occur without a fall, even if there is severe osteoporosis. Home environment is very important. Assess your home for hazards. i). All rooms in the house should be well-lighted .ii). Remove obstacles in path, keep electrical cords against the wall, and clear excess furniture and anything else that could trip you. It is better to have a bar to hold while walking. Make sure every room and passageway is well lit. Going out at night without a torch or lantern also a common cause of fall. iii).Bath room slippery tiles is an important cause of fall. Change to non-slippery tiles. v). Your dress code (Saree, lenga, Dhoti):Long Lenga or Dhotee in gents and Saree in females is also a cause of stripping. Ladies should use Panjabi dress and gents use shorter Lenga.
6.Check your eyes. Have an eye exam every other year, or 6 monthly if you have diabetes or an eye disease. Change glasses as required.
7.Watch your medications. Some drugs may cause feeling of weak and dizzy and can increase your risk of falling. Consult your doctor about side effects caused by your medications.
8.Stand up slowly. Getting up suddenly can cause drop in blood pressure and giddiness.
- Use a cane, walking stick or walker.If you don’t feel steady when you walk, use one of these aids might help.
- Neurological diseases: Regular health check- up is very important. Diseases like Parkinson’s disease or stroke may cause a fall due to imbalance
11.Osteoporosis. Osteoporosis can be prevented by diet, exercises and taking some pills ( Calcium, vitamin D and anti-osteoporotic drugs like alendronate and inj.Teriparatide). If osteoporosis is detected it is very urgent to start medical treatment and to prevent fall. The treatment consists of: 1.injection Teriparatide 2. Inj Zolandronic acid or Alendronate tablets or injection Denosomab. 3. Vitamin D, calcium protein. If you already have one fracture, to prevent another fracture you must take full treatment of osteoporosis.
- Diabetes. If you have diabetes regular health check up and control are essential.
Types of hip bone fractures
There are mainly 3 types of hip fractures. Type 1. Fracture neck of femur which occurs below the ball, the head of thigh bone. This is covered by capsule of fibrous tissue. Therefore, it is also called as intra-capsular fracture. Type 2. is inter-trochanteric fracture which occurs between greater and lesser trochanter. Type 3 is subtrochanteric fracture below the lesser trochanter. (fig 1) These 3 types of fractures behave entirely differently. The treatment of these fractures also varies. We will discuss here only fracture neck of femur
Three types of fractures of hip bone A). Fracture neck of femur. B). Inter-trochanteric fracture. C). Sub-trochanteric fracture.
Fracture neck of femur
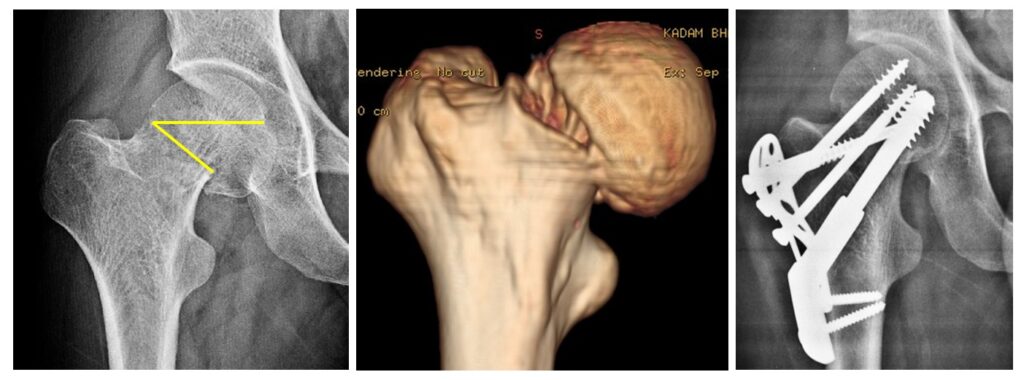
The hip fracture you have sustained is called “Intra capsular fracture neck of femur”. The area is situated just below the ball (femoral head) of the ball-and-socket joint. This is a serious fracture because after fixation of fracture, in 30% cases complications occur and reoperation of replacement is needed. Replacement also has some problems. There are 2 types of neck fracture-type I-(Fig 2) is horizontal fracture. Type II is vertical fracture (Fig 3) which is more dangerous, because non-union is more common. Therefore, requires a different type of treatment than horizontal fracture.
Fig.2. A pleader, 30 years old had a fall from 10 feet height. A). X-rays show fracture neck of femur (Hip fracture). A horizontal type. B). CT scan shows displacement of fragments C Fixation of fracture with screws and plate. The fracture united
Fig 3. A case fracture neck femur vertical type. This fracture was converted into a horizontal type by doing an osteotomy, called as valgus osteotomy. The fracture united uneventfully without any complications.
Symptoms of fracture neck of femur
1 After hip fracture there is pain in the hip joint and in the upper part of thigh. In the elderly, pain in the hip joint and groin and inability to stand is usually indicative of a hip fracture.
- Depending on the severity of the injury, the patient may or may not be able to stand up or walk or even turn in bed. In some patients, when the fracture fragments impact into one another, may be able to walk but with some pain. If an elderly person is unable to walk with hip pain after even a minor or trivial injury suspect hip fracture and have an x-ray of the hip urgently; because, if fracture neck femur is treated as early as possible, the result are better. Delayed surgery is associated with more complications.
- Any movement of the leg is very painful. Turning in bed may be very painful
4 There may be bruises and swelling around the hip.
- The affected limb may be shortened.
6 The affected Limb is in an externally rotated position.
What investigations are needed?
Plane x-rays usually diagnose hip fracture. In some cases x-rays do not show any fracture. Therefore, Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans may be necessary as they are most sensitive for the evaluation of fractures, particularly occult or fractures of neck of femur. CT scan gives information of the amount of displacement, comminution and position of fragments, which will help the surgeon to plan the surgery. Physician, anesthetist and if needed other consultant are consulted.Other investigations like blood tests, ECG and other investigations are needed to detect the fitness of patient for surgery and to find any other comorbidity.
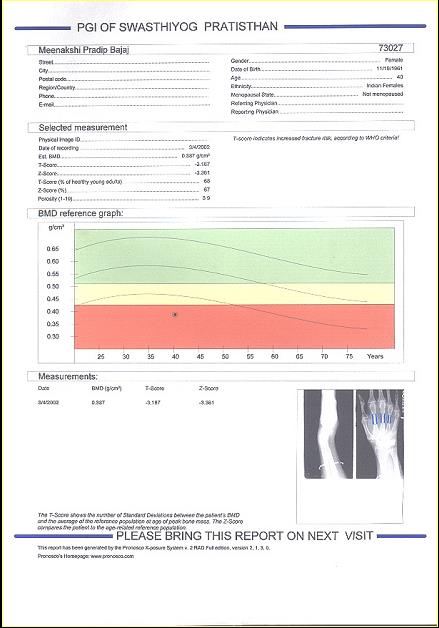
DEXA (Fig 4) scan is an important investigation to find the quality of bone (osteoporosis) which will help surgeons to plan treatment and post-operative care.
Fig 4. DEXA Scan. The black dot in the red zone shows severe osteoporosis, less than minus 2.5
Why FNF is a problem fracture?
Despite of great advances in fracture management, treatment of FNF is very controversial. Problems of this fractureare:1. It is unique bone on which tremendous forces act.2. Blood supply to the head of femur is damaged during injury. Therefore, the head becomes a dead bone It is called as avascular necrosis (AVN) which causes deformity of head and pain. AVN usually occurs after one year but sometimes it may occur even in the third year after operation. 2. This fracture is associated with complication of non-union more than any bone in the body. To avoid complications of treatment of FNF, fixation of fractures must be done as early as possible.3. FNF usually occurs in the elderly persons. Bed is worst place for old persons; Because they develop bed sore and a dreaded complication, pulmonary embolism. A hip fracture can reduce your independence and sometimes shorten your life.
Treatment
Most patients need surgical treatment. Medicines will not help. There are 2 types of surgeries.
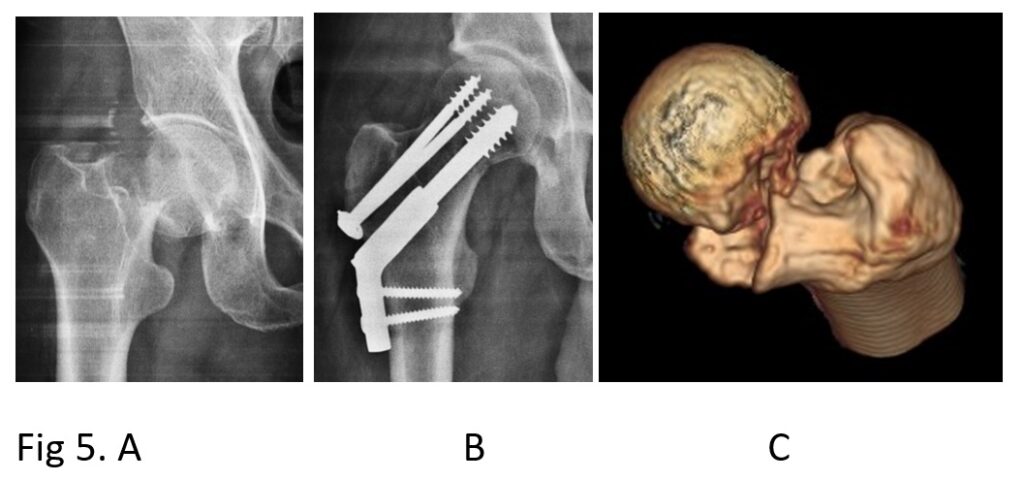
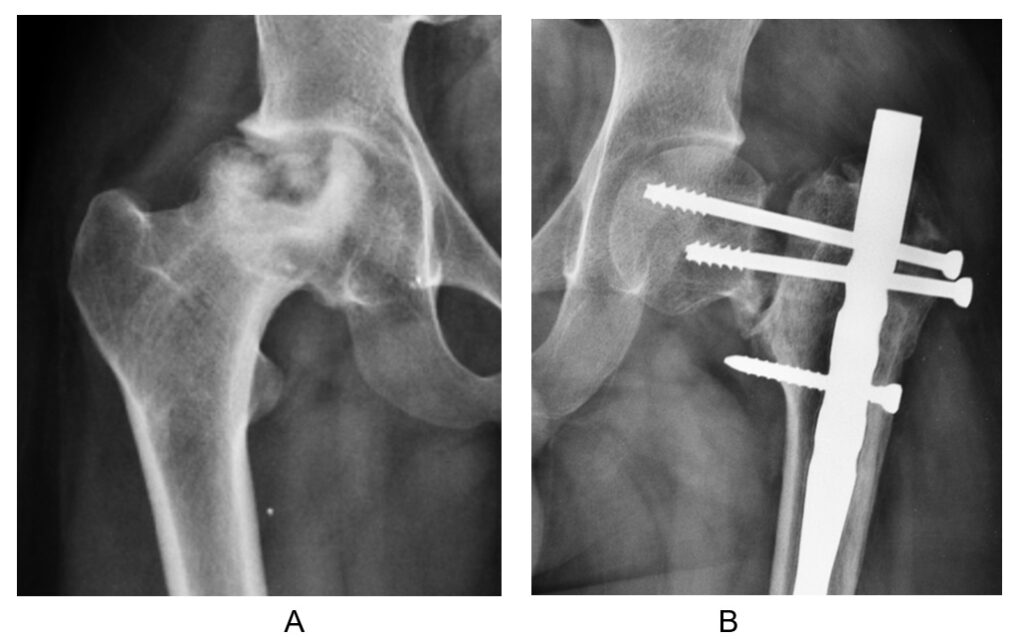
1 Fixation of head to the main bone. (Fig 5) The fracture is reduced as it was before fracture and both fragments are fixed with different types of screws and side plate so that they don’t move. Fixation is usually done in younger patients with good bone quality in the age group below 60 or 65 years.
A). Shows plane x-ray showing fracture neck of femur B Shows fracture united after fixation of fracture by screws and plate. C). Shows CT scan shows comminution of the fracture.
- Replacement: In this type of operation the ball (head) is removed and replaced with a metal ball. This type of operation is usually done in the age group above 60 or 65 years.(Fig 6)
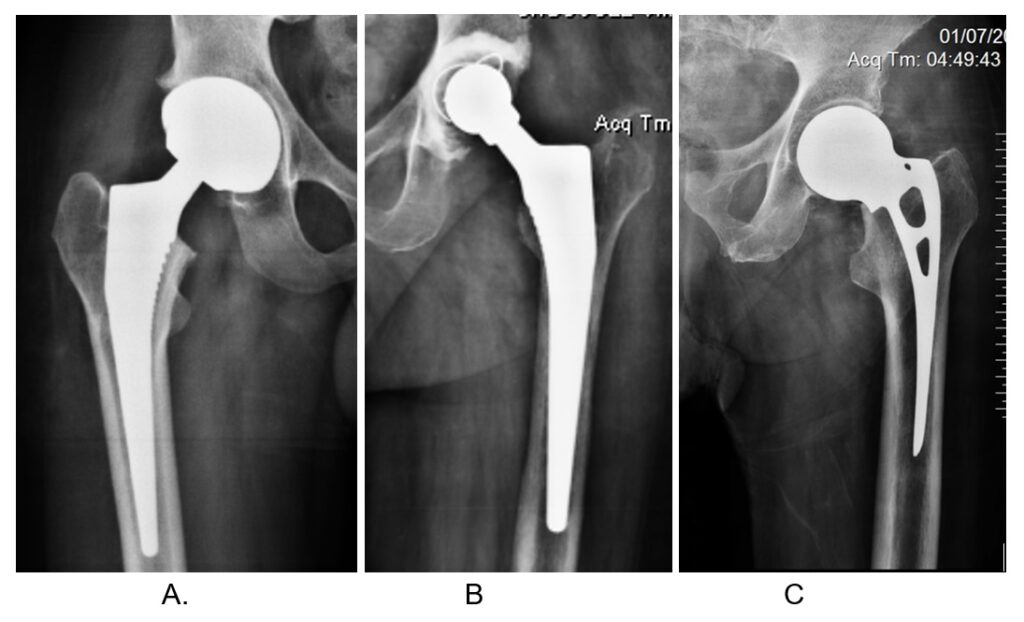
Fig 6. Three types of replacements A. shows bipolar replacement. B. shows total hip replacement. C shows unipolar replacement In all, the head of femur is removed and replaced by metal ball.
Decision whether to do fixation or replacement
The decision to treat femoral neck fractures with fixation or with replacement is controversial. The surgeon decides on the following considerations;
1 Age as described above. In younger patients fixation and in older patients replacement is done
- Quality of bone. DEXA scan will inform the extent of osteoporosis. Also, DEXA helps in planning surgery and helps in deciding the types of screws and plate to be used.
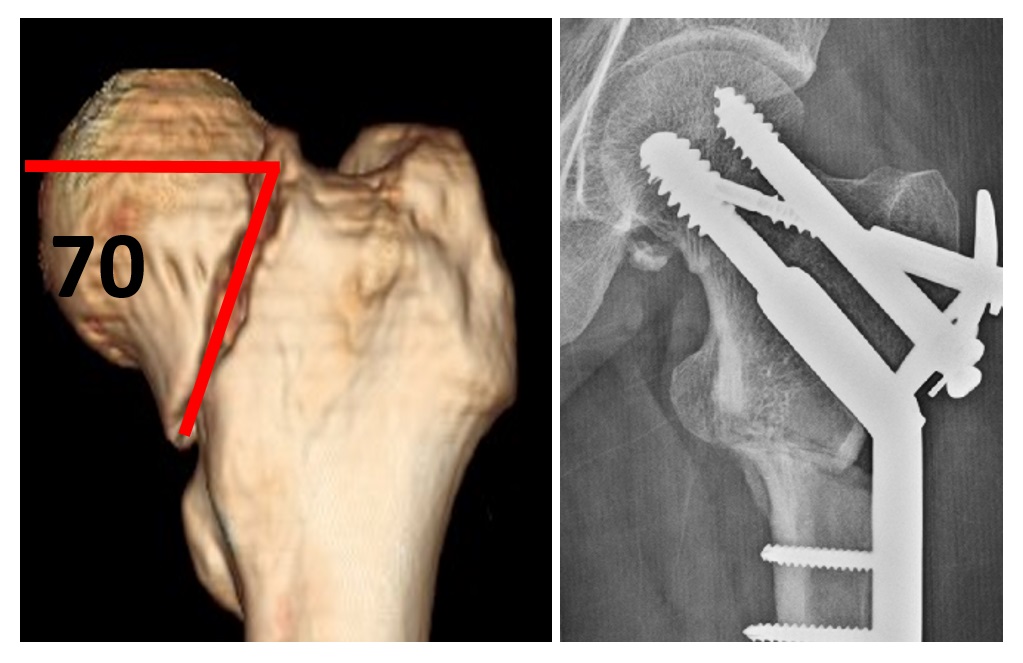
- Comminution. (Fig 5) How many fragments the fracture has? Fracture is vertical or horizontal? Whether the fracture is displaced or un-displaced? If displaced how much displaced? CT scan will help to answer these questions.
- How is the general condition of the patient ? How active the patient is? Patient is very active and doing heavy work or walking only in the house or non-ambulatory due other comorbidities. Are there any co-morbidities like heart disease, If the patient old is usually replacement is done.
- Patient’s demand. Proper counselling is done with the patient and his/her relations. Pros and cons of each type of operation, fixation or replacement, are explained in detail. Their decision also is taken into consideration.
- Financial aspect. Replacement is more costly.
The advantages of fixation are; 1. It is less invasive surgery, 2. less blood loss, and 3. less postoperative morbidity. 4 Less cost.
Disadvantages are: fixation treatment is associated with complications of non-union, avascular necrosis (Fig 7) and shortening of neck which occurs in about 20 to 30 % of cases. In 80 % of cases bone heals well. If the bone does not heal, the screws will backout as the fracture collapses. Non-union causes worsening pain in the hip. Late (after a year or more) avascular necrosis results from damage to the blood vessels that supply the femoral head. Six monthly x-rays should be taken up to 3 years to detect avascular necrosis. Fixation carries a higher risk of repeat surgery.
Fig 7. A. Shows of AVN. B. Shows non-union.
Advantages of replacement are 1. It offers fewer reoperations for non-union, implant failure, and avascular necrosis which will not occur 2.Elderly patient can be mobilized early; within a few days he/she starts walking. This is very important because if elderly person remains in bed for a long time he/she is likely to develop bed sore and dreaded complications like pulmonary embolism. He/she can be independent within a few days.
Disadvantages of replacement surgery are 1.It is a major surgery which results in more acute postoperative morbidity. 2. It is more costly 3. Prosthesis used for replacement also has a life of 10 to 15 years, it gets worn out and needs to be revised. 4 Dislocation is a complication in a few patients
All nondisplaced fractures, at any age, are treated with fixation by pinning. (2 or 3 pins)
Displaced fractures of inactive or non-ambulatory patients are treated with unipolar hemiarthroplasty. Displaced fractures in highly active patients are treated with total hip replacement or bipolar prosthesis.
Post-operative care after fracture fixation
- A very important step is to prevent another fracture in future, by treating osteoporosis and measures to prevent a fall. It is a common scenario that an elderly patient with one hip fracture treated, suffers from another hip fracture because of osteoporosis. Start with injection Teriparatide, inj Zolandronic acid or tablet alendronate or inj. Denosomab, vit D, calcium, high protein diet and exercises.
- Mobilization: (Fig 8). From day1 of surgery, start movements of foot and knee. Patient is allowed to sit up, stand or walk partial or no weight bearing with the aid of walker, as soon as he/she is able to do so.; This will prevent clotting of blood in the veins of leg, embolism and bed sore. If hip fracture keeps you immobile for a long time, the complications can include: Blood clots in your legs or lungs (pulmonary embolism, a serious complication), bedsores, urinary tract infections, pneumonia further loss of muscle mass, increasing your risk of falls and injuries
Fig 8. Mobilisation of patient on a walker.
Patient will feel better and becomes more confident that he/she will be able to walk and will be back-to-normal. After fixation of fracture neck femur usually patient is asked to use a walker for 3 months with touching the foot to ground in the first few weeks (no weight bearing) and then gradually increase weight bearing as pain is reduced. Weight bearing should be pain-free. Increase walking as much as you can without pain
3.Breathing exercises. Are important to prevent lung complications like pneumonia
4.Diet. Patient needs high protein diet
5.Drugs. Antibiotics, paracetamol for pain and other drugs as required. Some surgeons use injection Teriparatide for 3 months to stimulate fracture healing in the younger patient and continue it for 2 years for the older patient.
6.Sitting down. Sitting down with cross-legged or squatting should be done under guidance of treating surgeon
Complications of fixation and their treatment
1.AVN. After fracture blood circulation to the head of femur is reduced due to damaged blood vessels. When there is no blood supply to bone of the head, it becomes a dead bone. This is called as avascular necrosis of the head (AVN). (fig 7) and the head collapses as shown in the The patient may have pain and 2nd operation may be needed. If symptoms of AVN are troublesome the treatment is usually replacement.
2 Non-union. (Fig 7) As the bones are weak the screws that are inserted to hold the fracture become loose and fracture may not unite, in about to 15% of cases. The fracture may not unite because of poor circulation, shearing forces acting on the head, osteoporosis and many other causes. In 8o to 85 % of the cases fracture heals uneventfully and patient goes back to work. If nonunion occurs it is treated by an operation called valgus osteotomy in the younger patient or in the elderly patient by replacement
- Shortening of neck and limb: may occur due to collapse head. Shortening may cause shortening of limb, pain and limp
- Infection: Infection may occur in about 2 to 5% of the cases. The causes of infection may be a focus of infection present some – where else in the body, patient’s reduced immunity, poor operation room protocol or many other causes. If infection occurs it may need another operation to clear the infection and replacement of head.
- Clotting of blood in the veins and pulmonary embolism. Blood in the veins of leg may clot due to immobilization and other causes, resulting in swelling of the foot. Sometimes the clot may travel through circulation to the lungs in a serious condition called as pulmonary.
- Bed sore may occur if patient is not mobilised.
Post-operative care after replacement
1.It is very important that the elderly patients should start movements of the body. Sit up as early as possible after surgery and move limbs and hands and feet. Next day he / she should stand and try to walk with aid of crutches to pain tolerance. 2. Start breathing exercises. 3.Do not adduct the operated limb. 4 Walk with abducted limbs 5.Take high protein diet. 6. Do not squat or sit on the ground. Use commode or chair for toilet. 7. Medications as directed by your doctor.
Complications of replacement and their treatment
- Pain. Unipolar hemiarthroplasty like Austin Moore or Thompson prosthesis, results in acetabular erosion and pain. Treatment of painful hemiarthroplasty is total hip replacement.
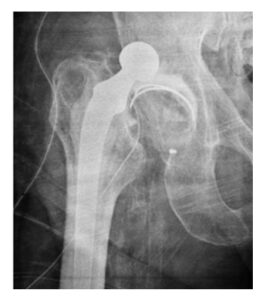
- Dislocation may occur with any type of prosthesis (Unipolar, Bipolar or Total). Treatment of dislocation is to reduce, usually by closed method but sometimes when closed reduction fails open reduction is required. (Fig 9)
Dislocation of THR.
Fig 9. X-rays showing dislocation of THR
3 Fracture of the implant may occur. The treatment for a fractured hemiarthroplasty is conversion to a total hip replacement.
4.Peri-prosthetic fracture of shaft of femur occurs due to osteoporosis and a fall. Treatment fractured bone is plating or revision total hip replacement.
5.Infection may occur which can be treated by clearing the infection and revision replacement
Treatment for a failed total hip replacement is a revision arthroplasty.
6.Movements of hip may be reduced
Newer implants
World’s 3 big implant manufacturing companies have developed newer implants for fixation of fracture neck of femur.
- Asculap has developed an implant called as Targon FN which has improved the results of fixation of FNF but still complications occur.
- Depuy-Synthes has developed a new implant called as Fracture neck system (FNS) which controls sliding of screws to 5,10 or 15 mm. The Trauma team at G.S.Kulkarni hospital also have developed a new implant which also controls sliding of screws to 5, 10 or 15 mms and is very much less costly and acts similar to Depuy-Synthes FNF.
- Smith-and nephew fracture neck Conquest which allows compression of fragments during post-operative period but is not available In India.
- Trauma team at GSKulkarni hospital have developed 3 newer implants for FNF
i). GSK controlled DHS which is similar to Depuy- synthes FNS but is of a different type than FNS and is cost effective.
- ii) GSK locking DHS which locks the screw to the plate and does not allow sliding. This is used when the bone stock is good in younger patients.
iii) GSKT system. This type of implant is based on triangle (strut) principle.
Imported implants are much costlier than GSK implant.
All these newer implants need to be proved that they are good on long term bases.
Summary
A fracture neck femur is a serious injury, with complications that can be life-threatening. Fortunately, it is a preventable fracture by treating the main causes of fracture, which are osteoporosis and a fall. The fragility of bone is prevented by some medication, proper diet and exercises. FNF should be treated as early as possible by surgery because the results are far better with early surgery. Younger patients are treated with fixation of fracture and elderly patients are treated by removing the head of femur and replacing it with a metal ball. Results of modern treatment of FNF are very good.